记录一次Nginx使用的坑
情况描述
https甲方配置了已经绑定到我们8082端口了,Nginx如何配才能让自己的请求通过这个端口在本地无证书的情况下变成https。
使用环境
Docker安装最新版Nginx,并映射到各自的80端口,做好了文件映射
1
| docker run -p 80:80 --name nginx --restart=always -v /opt/docker/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf -v /opt/docker/nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d -v /opt/docker/nginx/html:/usr/share/nginx/html -v /opt/docker/nginx/logs:/var/log/nginx -d nginx
|
坑一
不论怎么配置80端口的代理,永远不生效,指定root目录后依旧是展示Nginx启动页,换了资源目录、配置全局root、换成alias都无效。以下是配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
root /user/share/nginx/html/buildingNavigationFront;
server{
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name 12;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html/buildingNavigationFront;
index index.html index.htm;
add_header Content-Type "text/plain;charset=utf-8";
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Credentials' 'true';
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Methods' 'GET, POST';
}
}
}
|
然而,原因很简单
1
| include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
|
这句话指定了一个默认配置文件,打开这个默认配置文件会发现它自己代理了80端口,所以你的配置会被他覆盖,永远无法生效。这其实是Docker的锅,他会自动把这个配置写进去,但是在服务器里直接yum安装Nginx是不会有这项默认配置的。
坑二
解决了坑一后,代理80端口转发到8082,指定访问8082端口返回的资源目录。重启Nginx,终于不是Nginx的启动页面了,变成了长时间未响应的错误信息返回页。呵呵了。
在把搜索引擎敲烂后,终于找到了原因。其实也很简单,但是也很容易疏忽。
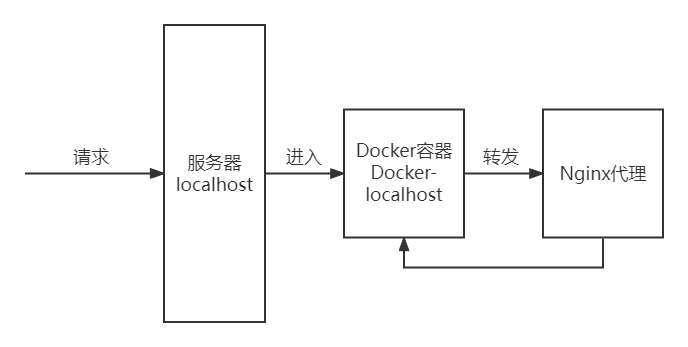
如下图,由于Docker容器化部署的特性,使用Nginx代理并映射80端口后,转发到的是Nginx容器下的资源目录和端口,所以如果这个Nginx容器下的目录和配置文件的目录对不上,就会导致错误。此外,如果配置的目录在服务器而不在容器,就需要在nginx.conf把代理地址设置为服务器的公网ip地址,而不是localhost,否则会转发到容器里去。
坑三
类似坑二,https甲方配置了已经绑定到我们8082端口了,但是代理之后通过80访问依旧无效。配置大概如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| server{
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
add_header X-Frame-Options ALLOWALL;
proxy_pass http://localhost:8082/;
}
}
server{
listen 8082;
server_name xxxxxxx.com;
location / {
root /user/share/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
|
坑二已经说过了,这是会转发到Nginx容器里去的,所以proxy_pass对应的地址应该是公网ip的8082端口,而不是localhost。
修改之后,依旧不行,此时已临近崩溃边缘。冷静下后,想到是说不定是防火墙的问题。
1
| firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
|
果然,列出的端口里没有80(明明之前开了)和8082。
1
2
| firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
firewall-cmd --reload
|
打开端口之后在测试,大概率应该已经成功
自己的解决方案
为什么说大概率呢,因为到达那步之后,我依然没有达到目标,但是这时的配置我自己已经找不出逻辑上的问题了,可能是配置乱了。最后总结出一个结论,不要用Docker去安装代理类的中间件。我已经放弃使用Docker来部署Nginx了,最后干脆删除了整个Nginx容器。直接在本地部署Nginx。
本地部署完Nginx,安装编译后,打开/usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf(默认路径),发现没有坑一说到的默认配置,舒服。配置好80端口和8082端口。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8082;
}
}
server {
listen 8082;
server_name xxxxxxx.com;
location /navigator {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8020;
}
location / {
root /opt/docker/nginx/html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
|
访问https://xxxxxxx.com/资源目录
成功本地无证书配置https